RESOURCES
PART DESIGN - RESINS - GLOSSARY - FAQ
PART DESIGN - RESINS - GLOSSARY - FAQ
Injection Molding Part Design
Wall Thickness
Ideally, the entire component should be a uniform thickness. As designed
As designed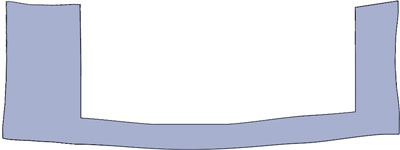 As molded
As molded
As a general guide, wall thicknesses for reinforced materials should be 0.75 mm to 3 mm, and those for unfilled materials should be 0.5 mm to 5 mm. Voids, sink and warp are a common result of a varied wall thickness.
Avoid Solid Shapes
Parts that might be made as solid shapes in traditional materials must be formed differently in plastics.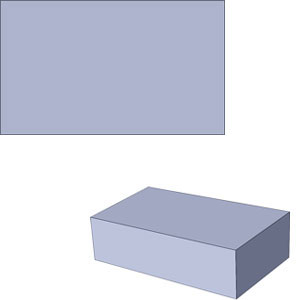 Wrong
WrongThick solid section.
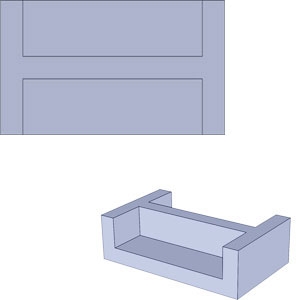 Right
RightCored out to thin uniform wall.
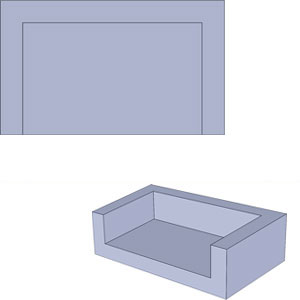 Right
RightCored out to thin uniform wall.
Transitions
Ideally, the entire component should be a uniform thickness. In practice that is often not possible. If a variation in thickness is required, it is important to keep this variation to a minimum. A plastic part with varied wall thickness will experience differing rates of cooling and shrinkage. This may result in a warped and distorted part. Tight tolerances may be impossible to hold. Wrong
WrongThick solid section.
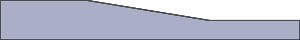 Wrong
WrongThick section but better transition.
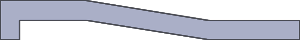 Best
BestCored out to thin uniform wall.
Corners
A properly designed corner increases the quality, strength and dimensional accuracy of a part. Smooth curved corners help plastic flow in the mold by reducing pressure drops.t = Wall thickness. General corner radius standards preferably should be in the range 0.6 to 0.75 times wall thickness. Worst
Best
Worst
Best
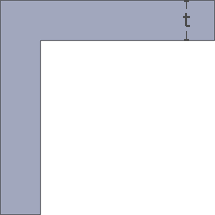 Internal: Sharp
Internal: SharpExternal: Sharp
Result: Uneven wall thickness.
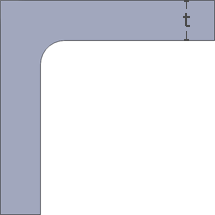 Internal: Radius = 0.6t
Internal: Radius = 0.6tExternal: Sharp
Result: Uneven wall thickness.
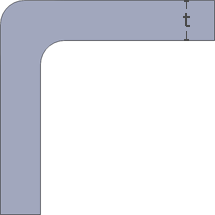 Internal: Radius = 0.6t
Internal: Radius = 0.6tExternal: Radius = 0.6t
Result: Uneven wall thickness.
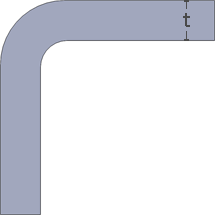 Internal: Radius = 0.6t
Internal: Radius = 0.6tExternal: Radius = 0.6t + t
Result: Even wall thickness.
Rib Thickness
Adding ribs is the best way to add strength to a part. Use ribs in place of increasing the wall thickness.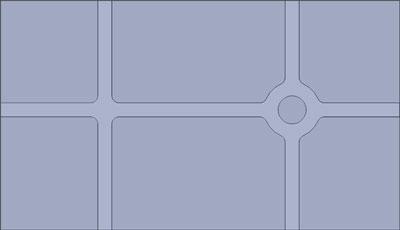
- Rib thickness should be 50 - 75% of the wall thickness.
- Fillet radius should be 40 - 60% of the rib thickness.
- Rib depth should not be more than 5 times the rib thickness.
- Taper ribs for mold release.
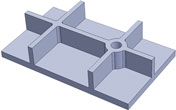
Rib Root Thickness
Ribs create thick sections at the root (defined by the circle below). This area is thicker than the nominal wall thickness and susceptible to sink.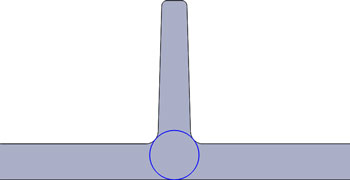
- Rib root thickness should not be more than 25% greater than the wall thickness.
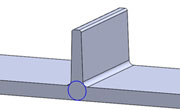
Boss Design
A boss is a raised stud feature that is used to engage fasteners or support features of other parts passing through them. Often used as means to connect two parts.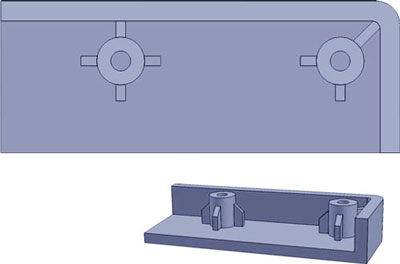
Right
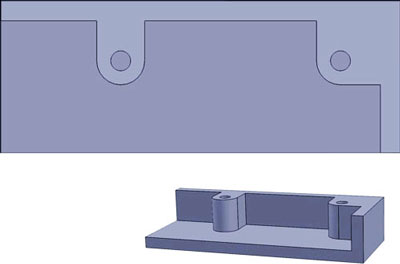
Wrong
There are many ways to design a good boss but thick sections should be avoided.
Living Hinge
A very thin section of plastic meant to be repeatedly bent. Connects two parts and keeps them together while allowing them to open and close.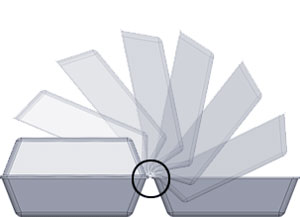 Living hinge
Living hinge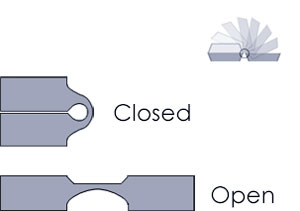 Correct
Correct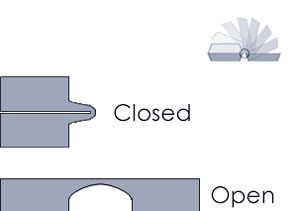 Wrong
Wrong- Polypropylene is the preferred material for living hinges.
- Avoid sharp corners.
- Relieve the back surface of the hinge.
- Commonly polypropylene hinges are 0.25 mm to 0.50 mm thick.
